Samples
Overview
Selecting Samples on the top menu brings up the main sample management view. Here, samples can be created, viewed,edited, analyzed, and removed.
What happens during sample creation?
Sample FASTQ files are copied into a new sample directory. The files will be compressed if necessary. Files associated with the sample can be viewed and downloaded under the sample detail tab.
Quality information is calculated from the library using FastQC and committed to Virtool’s database.
The FASTQ files and quality data are used for further analyses triggered by the user.
Browse Samples
Once you have imported one or more samples, they can be browsed in the main sample management view.
-
Navigate to the Samples view

-
Enter a search term in the search input
-
Use the status filters to further narrow the list of samples
For each workflow (Pathoscope, NuVs), the sample can have:
- no analysis available
- analysis in progress
- at least one completed analysis
Here we are looking for samples with names containing q10 that have a completed NuVs analysis:
-
Click on a sample to navigate to its detail view
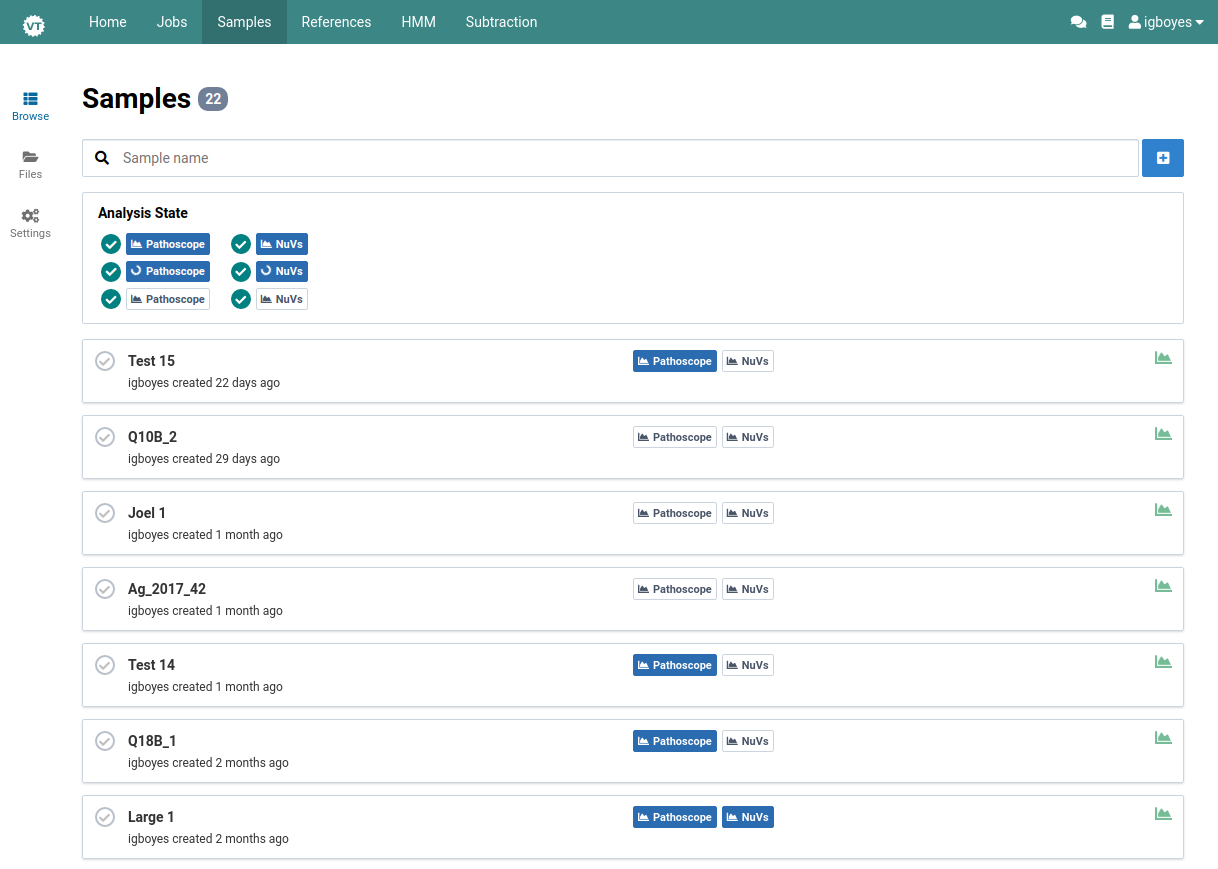
Here is the detail view for samples from the previous step: Q10A_2.
Start Quick Analysis
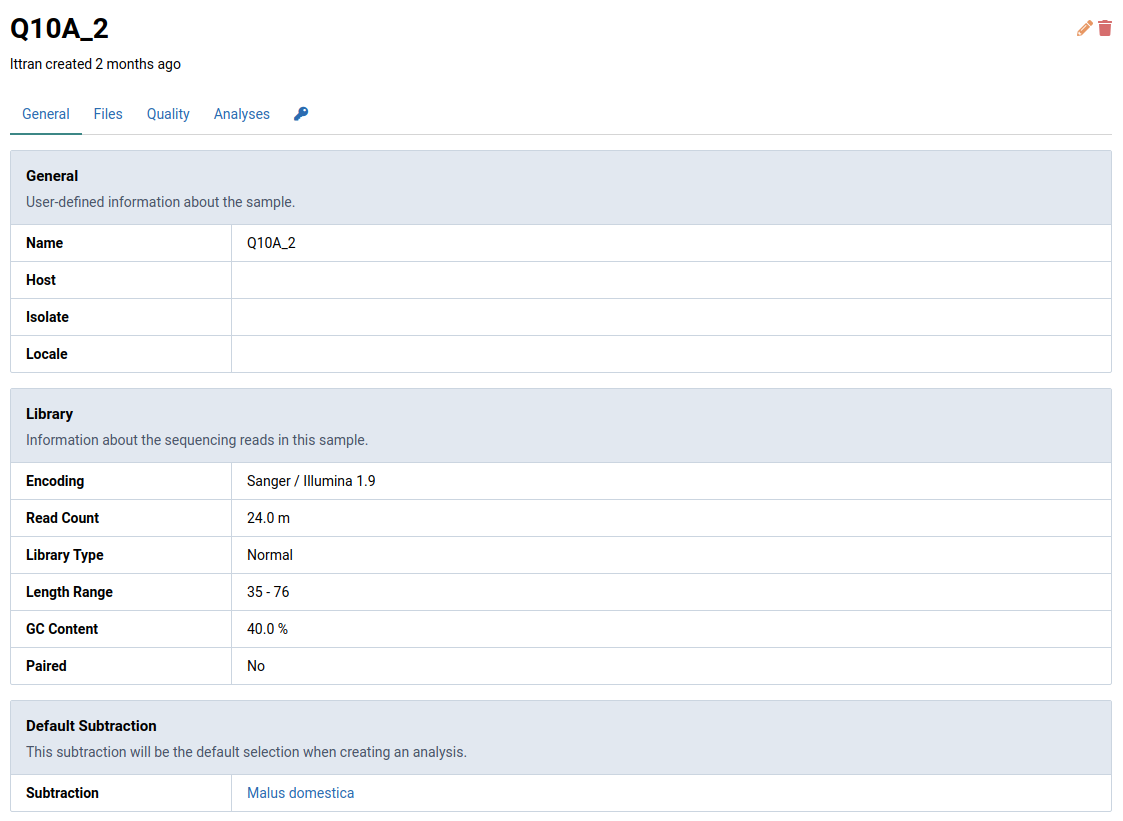
Quick analyses allows you to start analysis jobs for multiple samples at once.
-
Select the samples of interest and click .
An Analyze dialog box will appear.
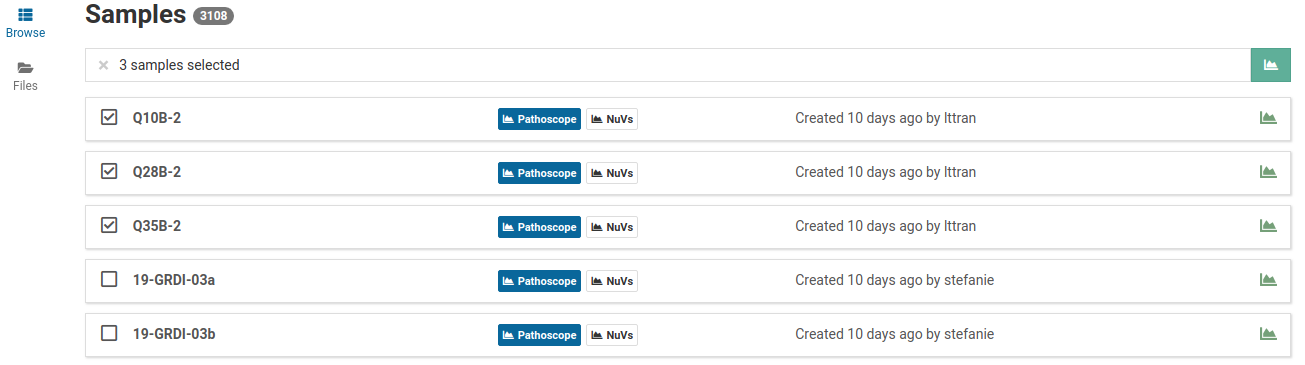
-
Choose the workflow(s) (PathoscopeBowtie or NuVs), subtraction, and reference(s) you want to use to analyze your sample(s).
Selecting multiple references will start a separate job for each sample-reference combination.
-
Click Start to start the analysis job(s).
-
Wait for the analysis to complete.
Once the analysis is running, you can view its progress under the Jobs tab.
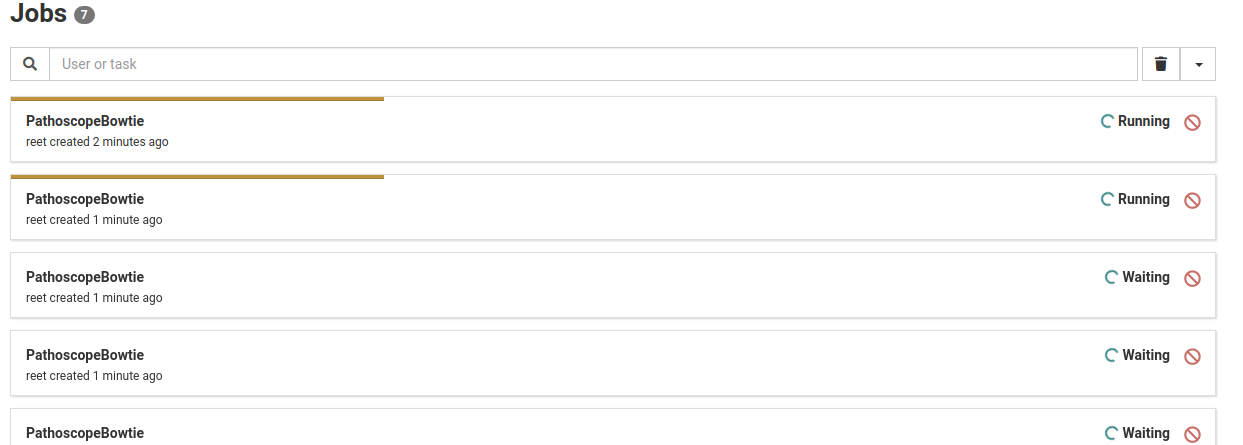
Create a Sample
-
Go to Samples view via the main navigation bar

-
Click Files in the left sidebar and upload a FASTA file.
-
Return to the Samples view and click to open the sample creation dialog
The file you uploaded should now be available in file list.
-
Populate the sample creation form.
You must set a unique sample name and read size. Read size can be set to either normal, sRNA, or amplicon. Subsequent analysis workflows will run using different parameters based on the read size setting.
The sample creation dialog allows you to set optional metadata including isolate, locale, and true host.
An default subtraction must be selected. This should be the subtraction genome most closely related to the true host for your sample.
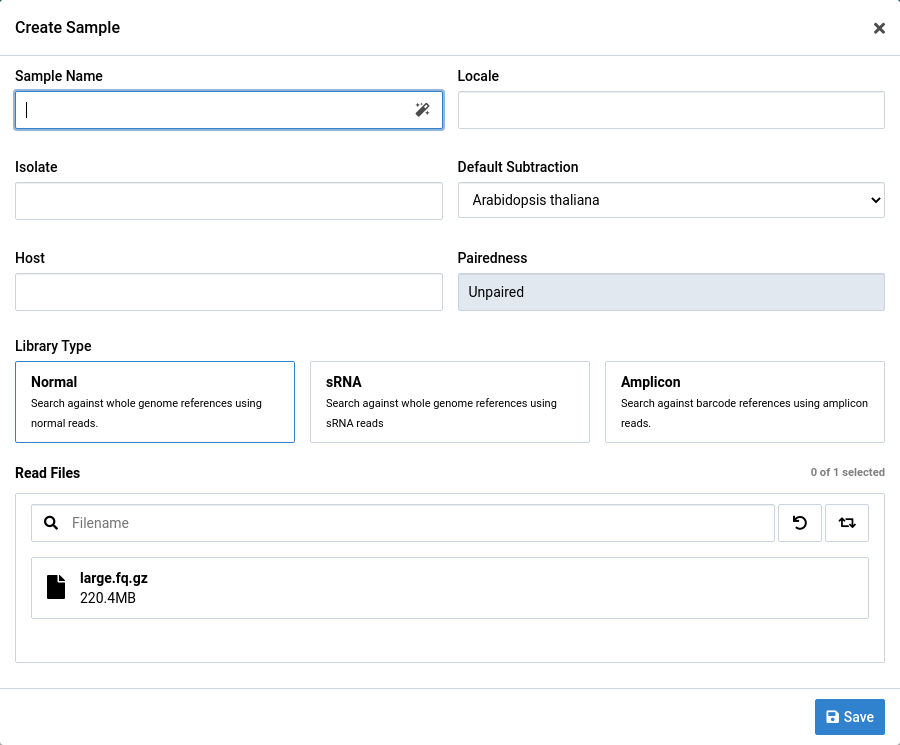
Paired and Unpaired FASTQ Data
Paired or unpaired FASTQ data can be used to create a sample.
Samples created from only one file are assumed to be unpaired. Paired samples must comprise two paired FASTQ files. Interleaved FASTQ files are not currently supported.
For paired data, make sure the file orientation labels (left and right) are correct before you create a sample. You can use the button to swap orientations.
Default Subtraction
The default subtraction for a sample will be pre-selected as whenever you create an analysis for that sample. You can find the default subtraction for a given sample at the bottom of its detail view.
For Banana bunchy top virus below, the default subtraction is Banana. This was the same subtraction that was selected when first creating this sample. Once a default subtraction has been made for a sample, you cannot change it.
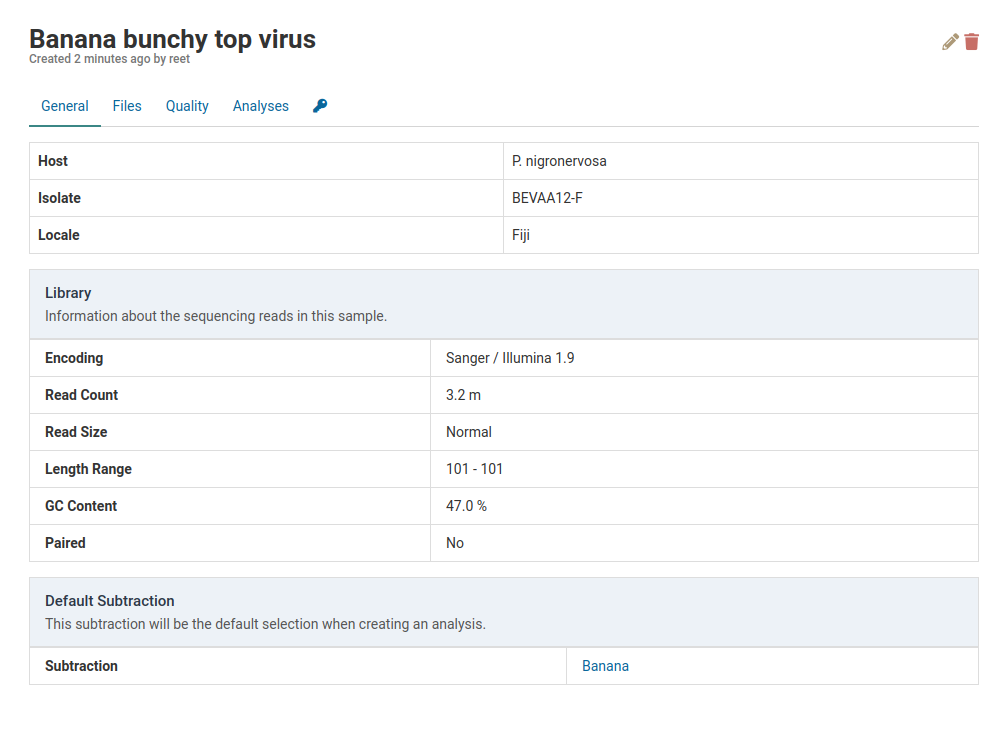
When you open an analysis creation dialog for the sample, the default subtraction (Banana) will already be pre-selected.
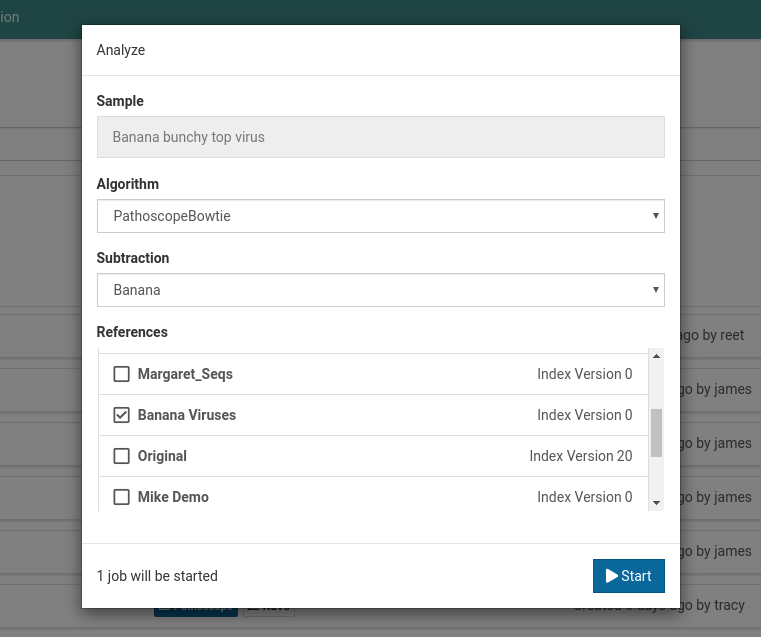
-
Click Save to create the sample and start the sample creation job.
You should immediately see a placeholder for your sample in the Samples view. The spinner indicates that the sample is still being created.

-
Wait for job to complete.
Your sample will look something like this when it is ready.

Interpreting Sample Quality
Quality metrics are calculated using FastQC during the sample creation process. These metrics are based on the raw data provided by the user.
The quality information can be viewed under the Quality tab:
You will see three different graphs on this page as shown below.
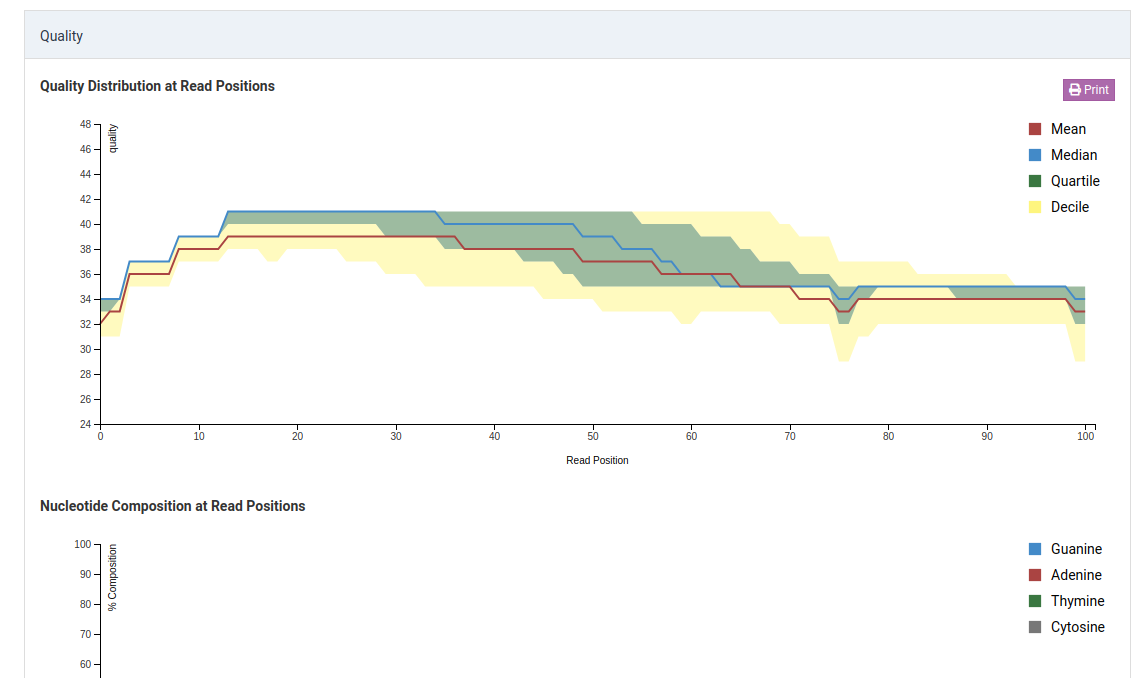
Quality Distribution at Read Positions
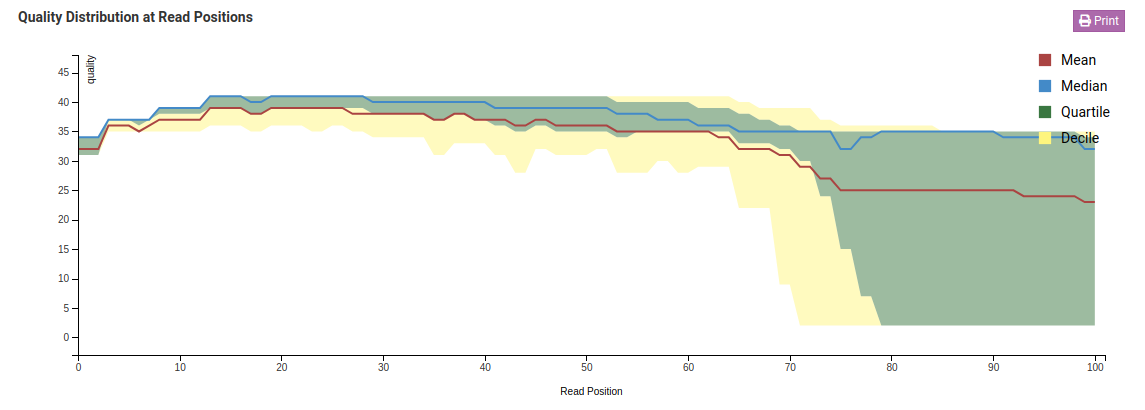
This graph shows the quality of your sample library. The Y-axis shows the quality score, the higher the better. The quality tends to decrease as the run progresses.
Median values of less than 25 or a lower quartile of less than 10 is concerning. In the case of the sample above, the quality of our sample library is fine and further analysis can take place.
Nucleotide Composition at Read Positions
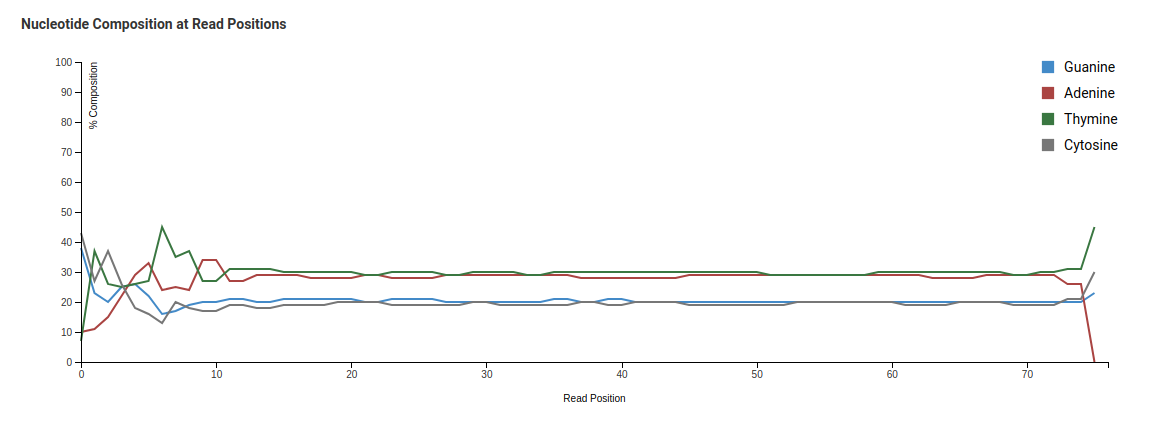
This plot shows the proportion of each base’s position in a file. In general, one should expect A/T to be roughly equal and G/C to be roughly equal. Viruses genomes are often unevenly distributed in composition and are usually A/T rich.
With all of the things being equal in a diverse library, you should see an even distribution of the four bases which doesn’t change with base position. Although the relative amount of G/C content will be determined by your library, but what you should see on the graph are parallel lines going across the plot.
Read-wise Quality Occurrence
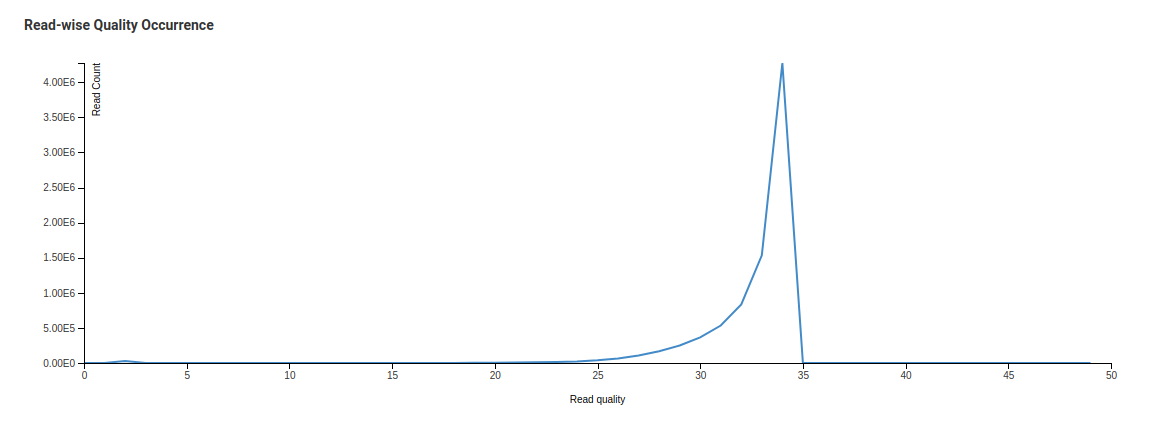
In this case we are taking every sequence and looking at the mean score across all the bases in that particular sequence. The distribution of those means are then plotted as shown above. All sequences should form one tight distribution (sharp curve) with universally high quality and no sequences of low quality. This sharp curve is the average quality per read. A mean quality below 27 is a cause for concern.
Edit a Sample
-
Click on Samples in the top navigation bar to see the sample listing.
-
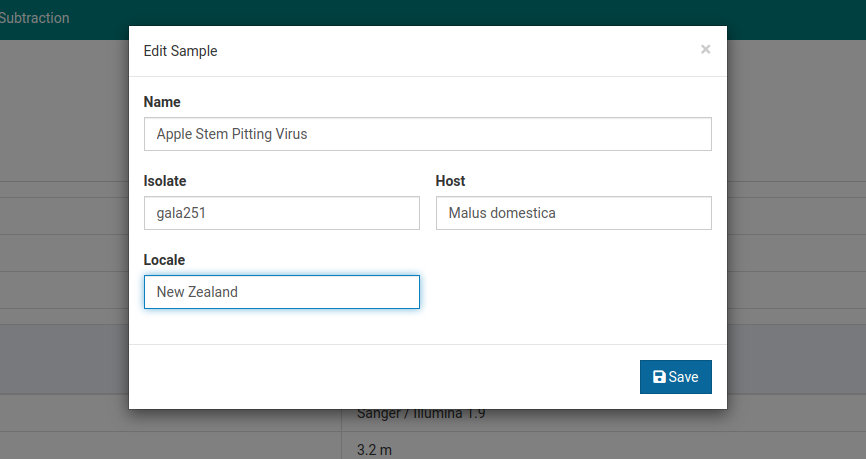
Click on the sample you would like to edit. Here we will choose Apple Stem Pitting Virus.
-
Click to open the sample editing dialog.
-
Make your changes and click Save to save them.
-
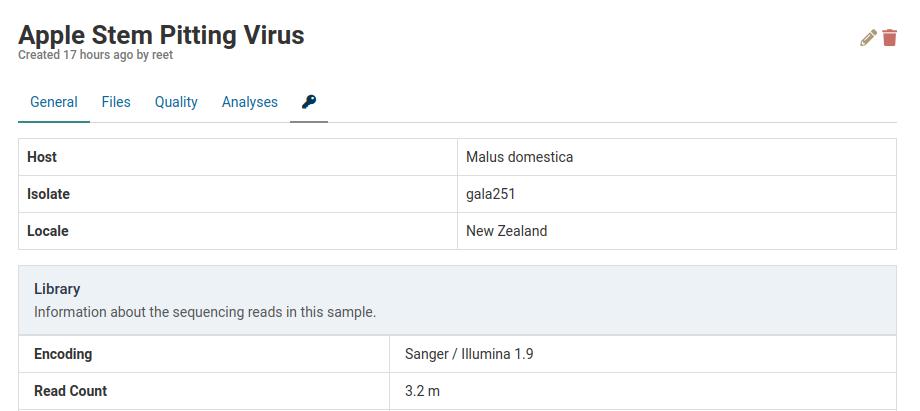
The changes will be reflected in the sample detail view.
Delete a Sample
- Click on Samples in the top navigation bar to see a list of available samples.
Click on the sample you wish to delete. Here we will delete Test A.
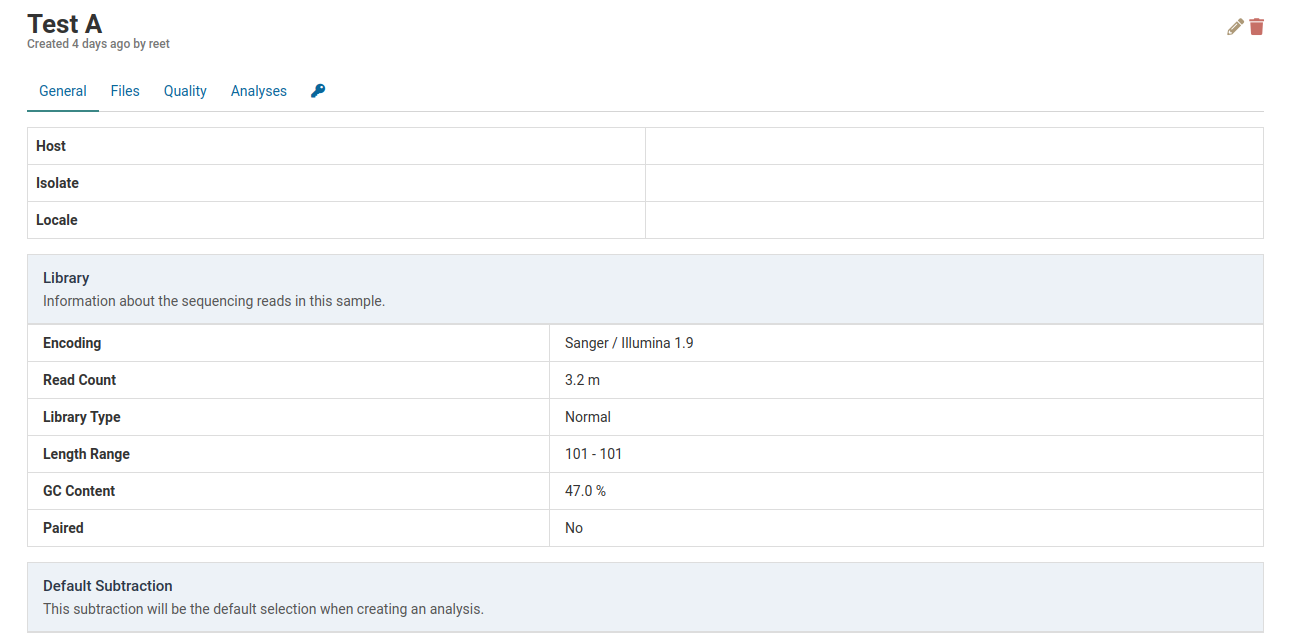
Click on the to delete the sample. A dialog box such as the one below will show up to confirm the deletion of the sample.
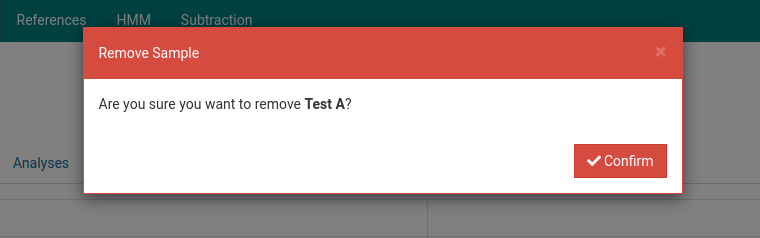
Click Confirm. The sample will now be removed from the samples list.
Download a FASTQ File
You can download the original FASTQ files used to create a sample. To do so, click on the sample of interest and then click Files.
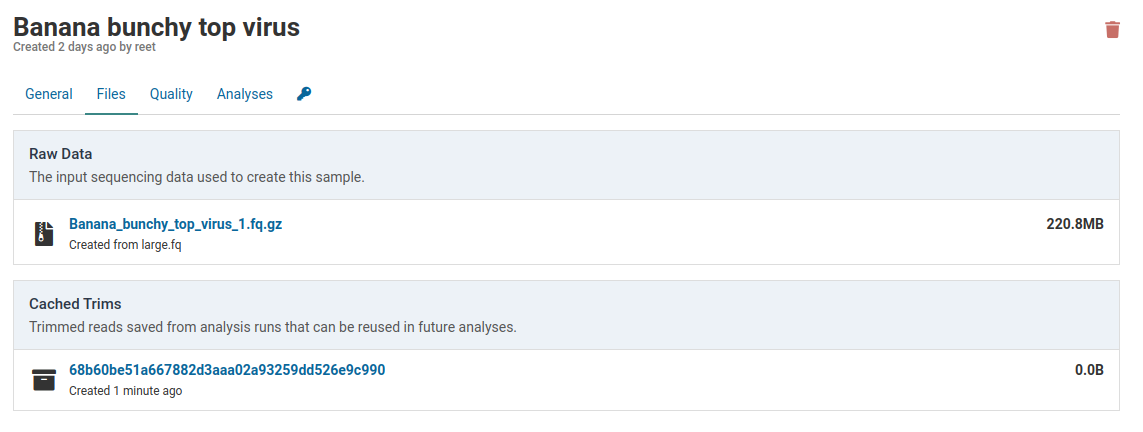
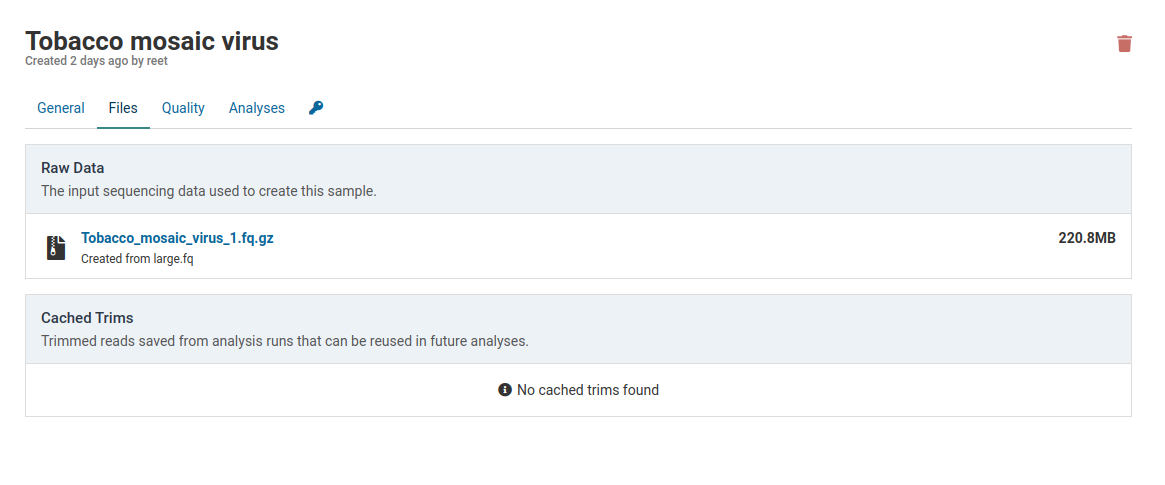
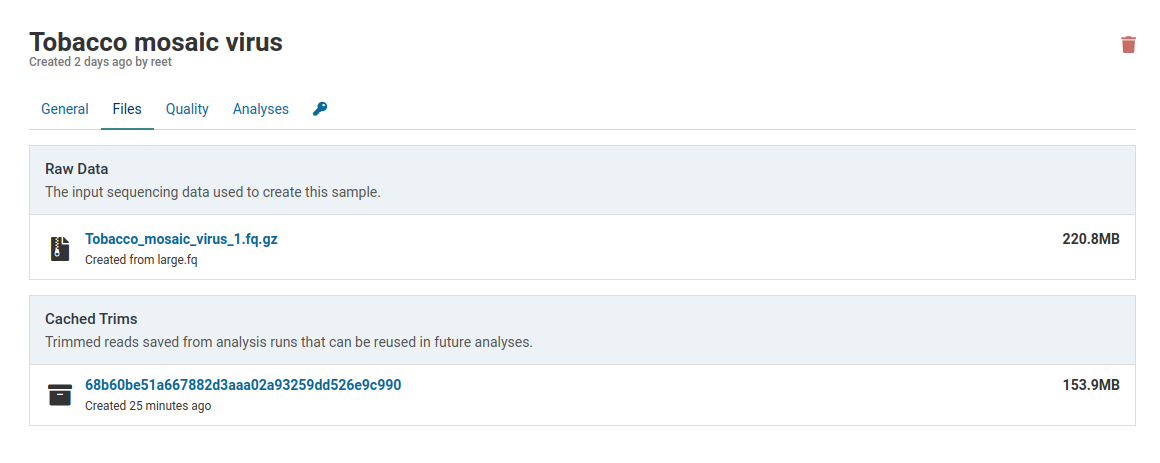
Click the link under Raw Data to download the FASTQ file that was originally used to create the sample.

Trim Caches
Sample data is automatically trimmed during analysis to remove sequencing artefacts and low quality regions. After the first analysis, the trimmed data are cached for reuse in future analyses that use the same trimming parameters. This saves running the trimming workflow steps for every analysis for a given sample.
A sample that has not yet been analyzed will not have any caches associated with it.
Running an analysis for this sample will create an analysis job. During the job the raw sample reads will be trimmed and cached for future analyses. As soon as trimming is complete the cache will be created.
Caches are always smaller than the raw data. This library was reduced from 220.8 MB to 153.9 MB. This is due to removal of low quality reads and localized shortening of reads with low quality ends.
When you click on the link under Cached Trims you will see all the parameters used by the trimming program as well as the name of the trimming command (skewer-0.2.2). The hash is a unique identifier for the program-parameters combination used to trim this cache.
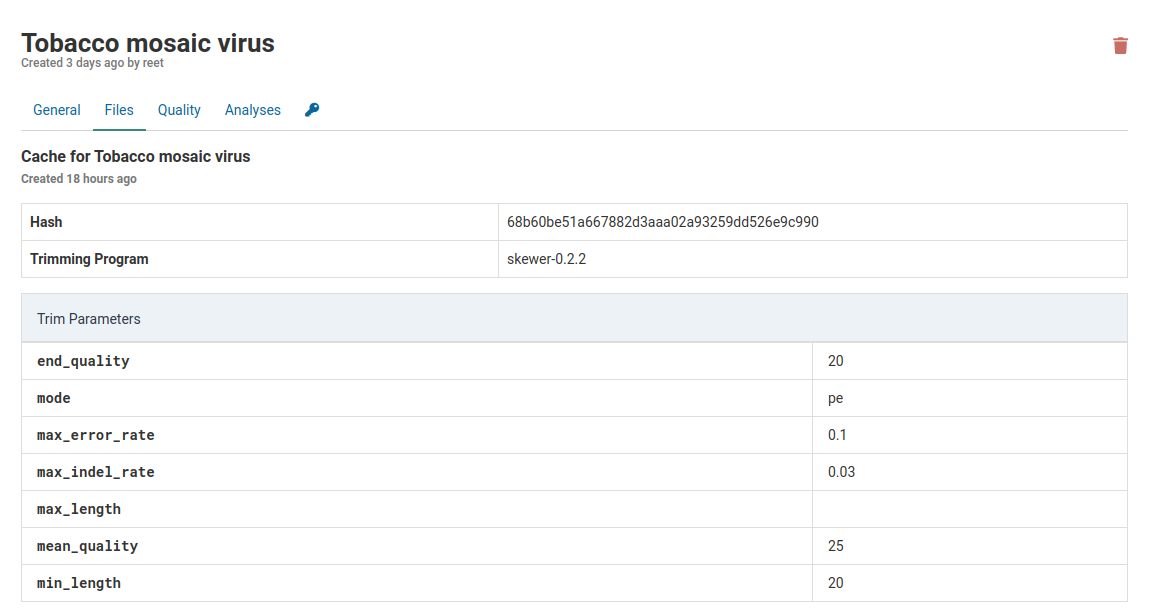
Additionally, below the parameters you will see the quality of the data that has been trimmed and cached.
Trim Cache Quality
Quality metrics are recalculated for reads trimmed during an analysis. The quality information is associated with the generated trim cache. Since low quality reads are discarded and low quality ends are removed, we expected the trim cache quality metrics to improve over those for the raw data.
Quality Distribution at Read Positions - Raw
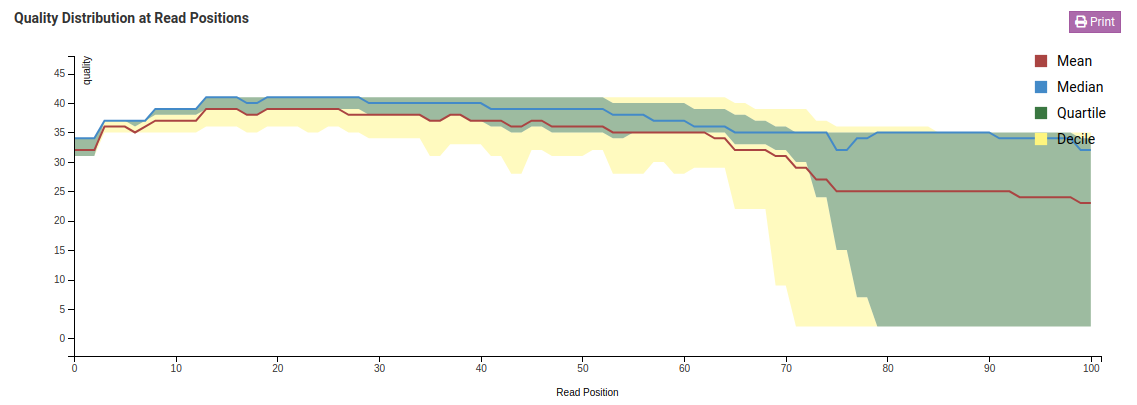
Quality Distribution at Read Positions - Trimmed
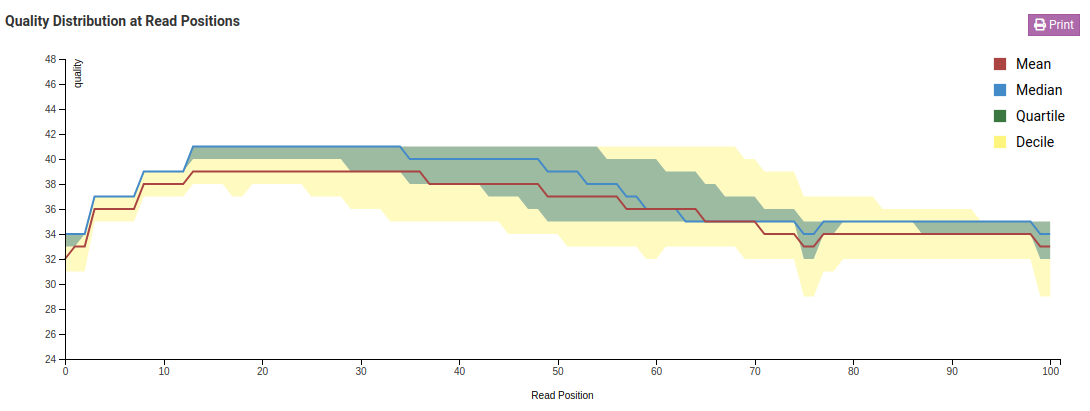
In the Quality Distribution at Read Positions - Raw chart we see that the mean base quality degrades as we get closer to the end of the read. This is a common issue in Illumina libraries. In the Trimmed charts we can see that low quality ends were removed resulting in a higher mean and minimum base quality.
Read-wise Quality Occurrence - Raw
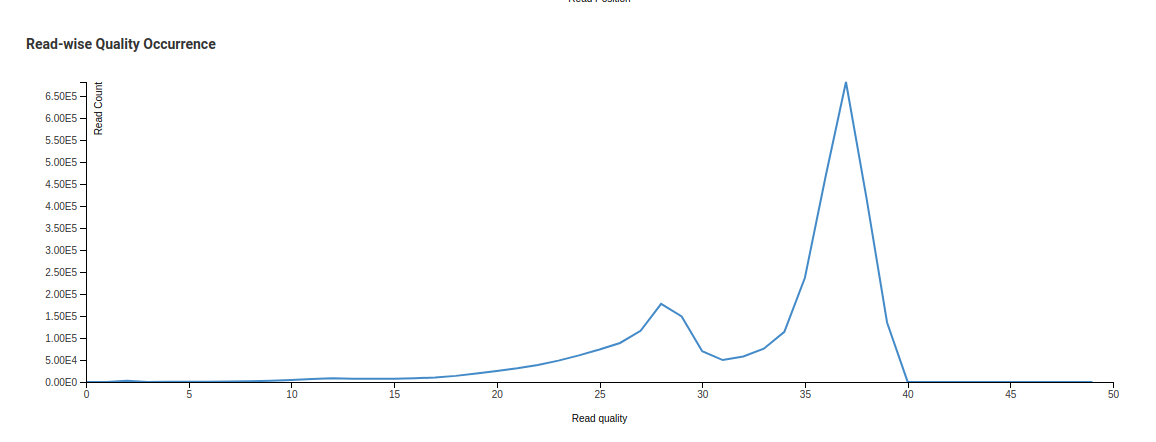
Read-wise Quality Occurrence - Trimmed
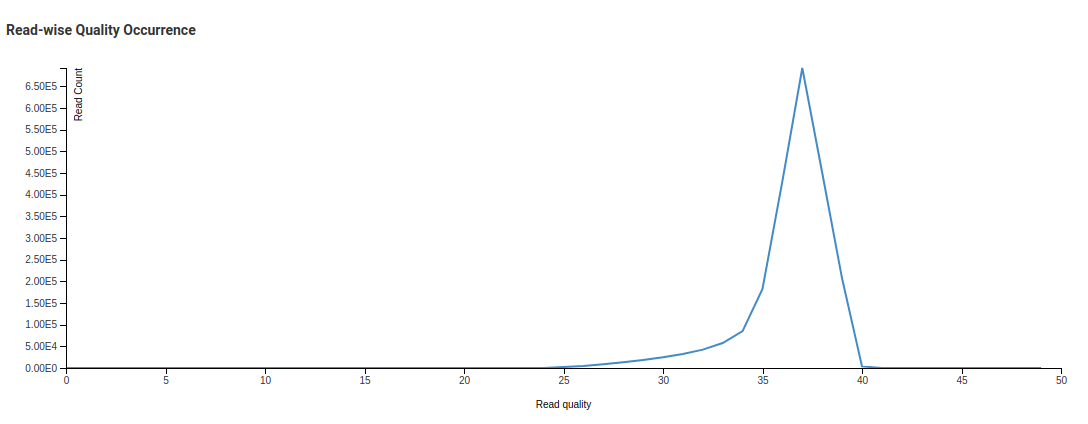
In the Read-wise Quality Occurrence - Raw image we see one small curve before a sharp peak. This is due to a significant number of reads with low mean quality being present in the library. The trimming process discards reads with low mean qualities. This is reflected in the Trimmed chart where the smaller peak is no longer present.
Rights
Concepts
Virtool allows for fine control of the rights users have to view or modify samples.
Management Levels
Rights can apply at four different levels.
| administrators | Members of the special administrator group. These users have full read and write access to all samples as well as the ability to manage the rights on any sample. |
| owner | The original sample creator. This user always has full read and write access to the sample as well as the ability to manage the rights on the sample. |
| group | The group that owns the sample. Read and write privileges can be independently set at this level. |
| all users | All users registered on the Virtool instance. Read and write privileges can be independently set at this level. |
Group Ownership
Each sample can be owned by a specific user group. This allows multiple groups of diagnosticians or researchers to keep their data private or safe from one another while sharing a single Virtool instance.
Samples are not required to have an owner group. The group can be set to None. In this case, group rights settings will have no effect.
Privileges
none
The management level (eg. group, all users) cannot read or write the sample. included users will never see the sample in the sample management interface.
This privilege is useful for completely isolating samples between separate groups of users.
read
The management level (eg. group, all users) can only read the sample. The included users will see the sample in the sample management interface and be able to view its general information, quality, and analyses.
They will not be able to edit or remove the sample and they will not be able to create new analyses. The elements in the user interface associated with the described actions will be hidden.
read & write
The management level (eg. group, all users) can only read the sample. The included users will see the sample in the sample management interface and be able to view its general information, quality, and analyses.
They will also be able to edit and remove the sample and create new analyses.
Management
The access rights for an existing sample can be easily changed by the sample owner or an administrator.
Access the rights management controls by clicking the tab in the sample detail view.
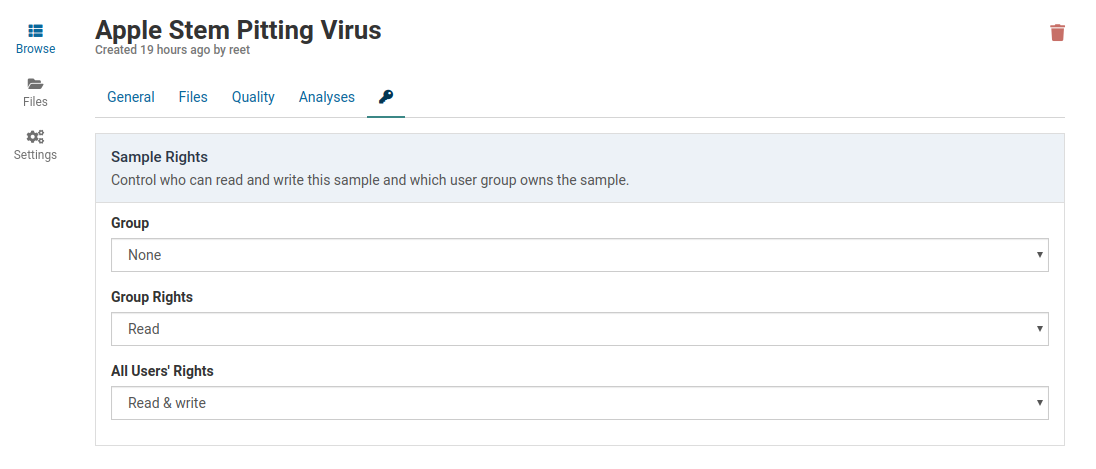
Default Rights
Samples have their initial access rights configured when they are first created. How these rights are assigned can be configured in the adminstrative settings.
- Go to the Settings | General view as an administrator.

Settings
Unique Sample Names
By default, sample names must be unique to the sample manager. This prevents confusion with duplicately named samples. It is possible to disable this feature. To do so, click Settings on the left sidebar under the samples overview page.
Check the Unique Sample Names box to ensure that every created sample has a unique name.
Default Sample Rights
These settings determine how rights are assigned to newly created samples. Sample rights in Virtool are reminiscent of UNIX permissions.
Sample Group
This determines how an owner group is applied to the sample when it is created.
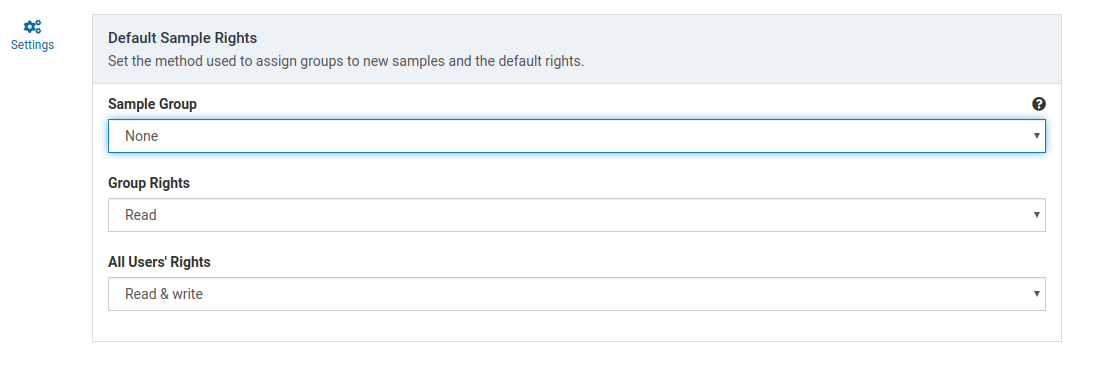
| None | No group owner is assigned. Group rights do not apply |
| Force Choice | The sample creator is forced to choose the owner group from their member groups |
| Primary Group | The sample is automatically assigned the creators primary group |
Group Rights
This setting determines how members of the owner group can interact with the sample. If the owner group is None, this setting has no effect.
Group Rights
This setting determines how members of the owner group can interact with the sample. If the owner group is None, this setting has no effect. Rights can be changed by sample owners and administrators at any time.

| None | Sample is not returned in searches and is not accessible by URL. |
| Read | Sample is returned in searches and is viewable. All editing interfaces are disabled and analyses cannot be started. |
| Read & Write | In addition to Read rights, editing interfaces are enabled and analyses can be run. |
All Users’ Rights
This settings determines how any Virtool user can interact with the sample. Rights for all users behave exactly as they do in Group Rights. Rights can be changed by sample owners and administrators at any time.